 About ChemoDOTS Server
About ChemoDOTS Server
What is the purpose of ChemoDOTS ?
The ChemoDOTS server provides an online platform for scientists engaged in hit-to-lead (H2L) optimization of a hit fragment.
Specifically, it facilitates the application of the growing strategy, wherein the hit fragment undergoes expansion through the addition of diverse substituents to enhance its binding affinity.
What are the benefits of ChemoDOTS ?
ChemoDOTS generates a diverse set of H2L candidate molecules while maximizing synthetic feasibility.
It helps scientists in achieving H2L optimization goals for drug development more rapidly and efficiently.
A focused chemical library is generated based on the used-defined hit fragment. All compounds in the virtual library feature the specified hit fragment with various added substituants offering a wealth of possible enhancements for improved molecules. Information about the commercial building blocks used to generate these compounds, achievable in one or two steps, is provided thereby facilitating their chemical synthesis by chemists.
Drug-like properties of the raw library can be tuned using various physico-chemical molecular descriptors.
The final chemical library is available in several standard formats including mol2 with atom types and partial charges allowing docking studies with the protein target.
How does it work ?
ChemoDOTS is based on our previously published DOTS approach (Hoffer et al., 2018).
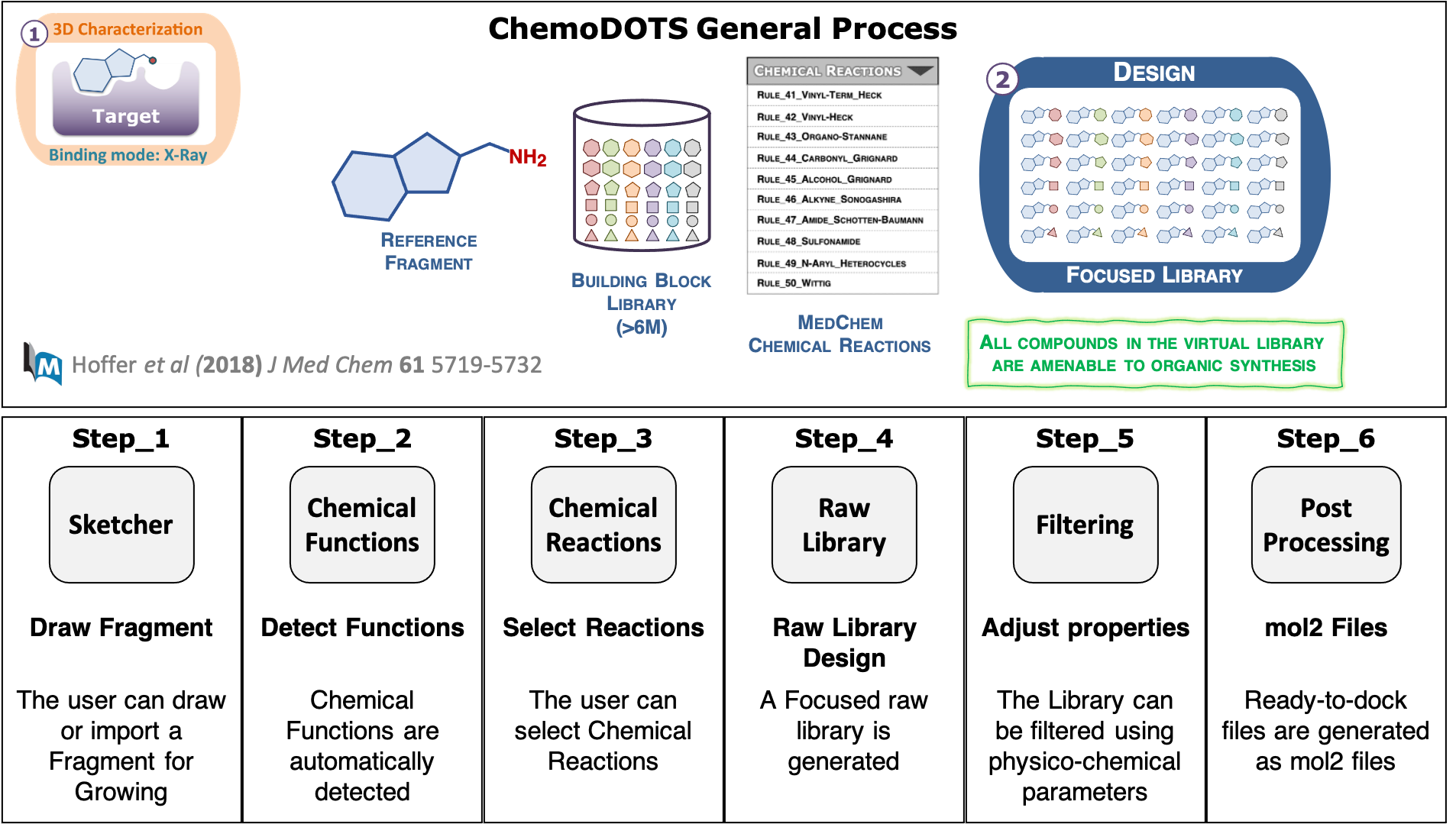
Building of Focused Chemical Libraries
Chemical libraries are built using a set of SMART-encoded organic chemical reactions based on a list of predefined reactions commonly-used in the pharmaceutical industry during the hit-to-lead optimization phase (Hartenfeller et al., 2011).
The ChemoDOTS workflow is summarized in the image below.
Post-Processing of the Raw Chemical Library
The post-processing can be divided into two phases: filtering and generation of ready-to-dock files.
Filtering of the raw chemical library
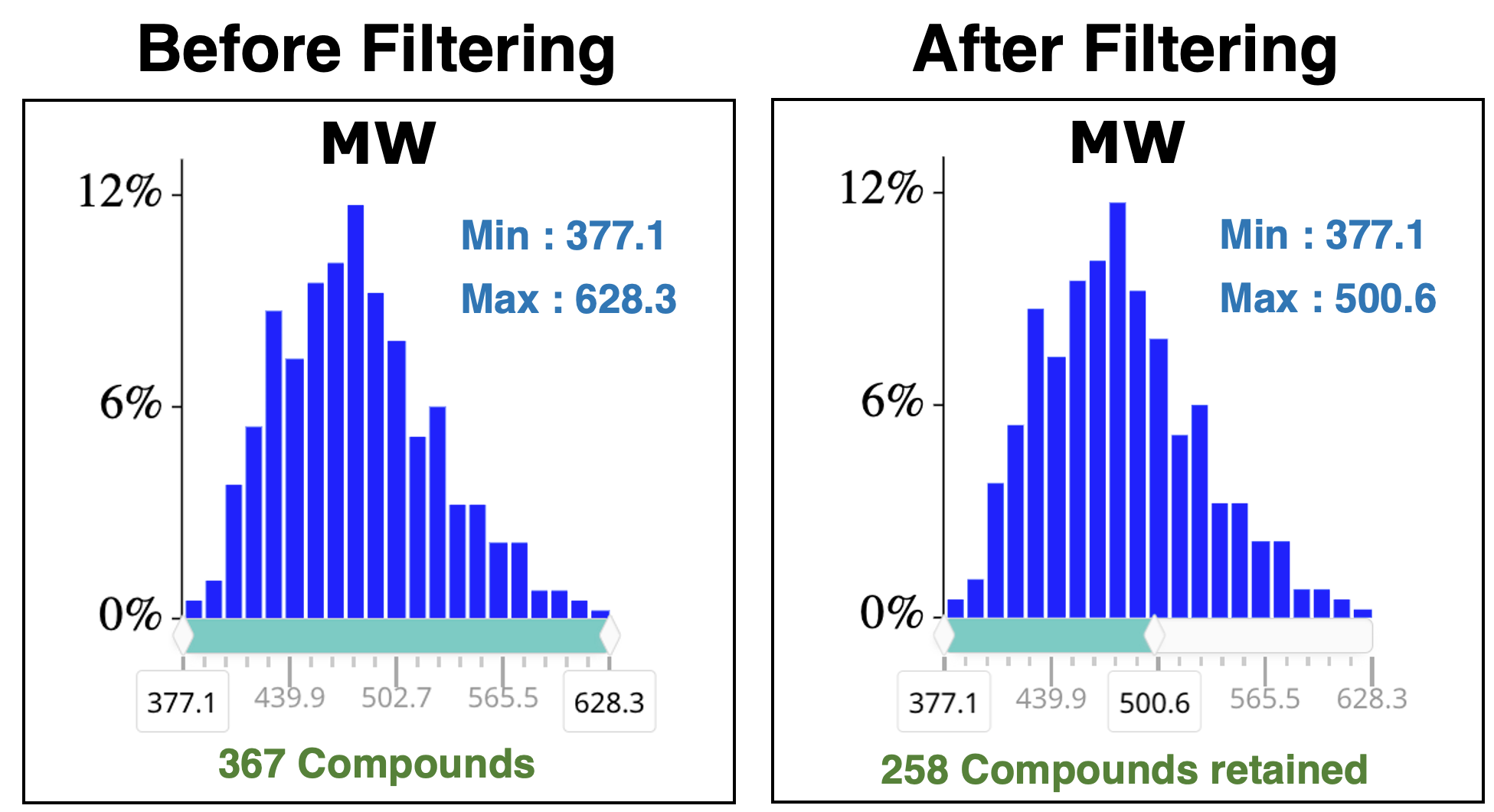
The raw Library can be filtered using standard physicochemical parameters to enhance the drug-likness of generated compounds or to reduce the number of compounds in the final library. Several molecular descriptors are available including Molecular Weight, LogP, Hydrogen Bond Donors, Hydrogen Bond Acceptors and Fsp3.
The user can adjust the min and max values of each parameter using a slider under the distribution of the given descriptor as shown below for the molecular weight. The total number of molecules in the final library is automatically updated.
Generation of a "Ready-to-Dock" Chemical Library
The last post-processing stage includes the computation of explicit stereoisomers and the generation of one 3D conformer for each compound. A virtual library compatible with most docking software is supplied as mol2 files with atom types and partial charges. Comprehensive reports and graphical representations are also provided.
How to Cite ChemoDOTS
To cite the ChemoDOTS web server, please refer to the following publication:
- Hoffer L, Charifi-Hoareau G, Barelier S, Betzi S, Miller T, Morelli X, Roche P. (2024) ChemoDOTS: a web server to design chemistry-driven focused libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae326. PMID: 38686808.
Poster presenting an overview of the ChemoDOTS approach
 Click on the image to access the poster
Click on the image to access the poster
 References
References
- Hartenfeller, M., Eberle, M., Meier, P., Nieto-Oberhuber, C., Altmann, K. H., Schneider, G., Jacoby, E., and Renner, S. (2011) A collection of robust organic synthesis reactions for in silico molecule design, J Chem Inf Model. 51, 3093-3098.
- Hoffer, L., Voitovich, Y. V., Raux, B., Carrasco, K., Muller, C., Fedorov, A. Y., Derviaux, C., Amouric, A., Betzi, S., Horvath, D., Varnek, A., Collette, Y., Combes, S., Roche, P., and Morelli, X. (2018a) Integrated Strategy for Lead Optimization Based on Fragment Growing: The Diversity-Oriented-Target-Focused-Synthesis Approach, J Med Chem 61, 5719-5732.

